Table of Contents
Did you know that an outdoor grow calendar could be the key to whether or not your crop thrives? While cultivating cannabis outdoors is the most popular choice, many farmers often overlook the importance of the growing conditions.
Does your state experience longer warm seasons or more intense cold snaps? Using a marijuana grow calendar for your outdoor crop is ideal for helping you stay ahead of your plant’s requirements.
Join us to take a closer look at the outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern and Southern states. We’ll also reveal the best strains for the conditions in those areas, helping you plan for a successful harvest.
Let’s dig in!
Why is a marijuana grow calendar important?
When growing cannabis indoors, you have full control over the cultivation conditions. If you time it all just right, you can force the plant to progress to the next stage in its lifecycle with the flip of a switch.
Unfortunately, this isn’t the case with outdoor cultivation—leaving your crops at the mercy of the elements. This is when an outdoor cannabis grow calendar helps you keep track of the requirements and get the timing just right.
When you start growing marijuana, the first thing to consider is that your chosen strain might not be compatible with the location. Whether using our outdoor cannabis grow calendar in Northern US or in the South, you’ll know what to expect each month.
Marijuana plants have specific requirements throughout their lifespan regarding soil, climate, and a cannabis feeding schedule. Allow our marijuana outdoor grow guide calendar to shed some light on the conditions for each month during the complete life cycle. </href="https:>
Marijuana grow calendar: Northern USA states
Let’s kick this off with our outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern states. While the growing season doesn’t start until mid-May, there’s more than enough to do while you prepare.
Remember that “if you fail to plan, you plan to fail.” Put the extra effort in now, and you’ll reap great rewards with a bountiful harvest.
This section will cover the outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern US states, with averages referring to New York, Chicago, and Seattle.

February
Average day length: 9.5–11.5 hours (8.5–10.5 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 22–51°F (-8–12°F in Alaska)
It may still be cold outside, but you can use this time to prepare for your pending crops. To dive into our outdoor cannabis grow calendar, let’s go shopping! Your required materials include:
- Soil
- Pots
- Nutrients
- Spray bottles and watering cans
- Cannabis seeds
Due to its short growing time, many cultivators prefer using indica strains for their crops.
If you live in an area that experiences longer frost and cold periods, opt to start your seeds indoors if you plan to clone. You can create ideal germination conditions by providing 18 hours of artificial light and maintaining temperatures between 68–77°F.
At this point in our outdoor grow calendar, we recommend that you start preparing the soil. Once the final bits of frost have cleared, you can aerate the soil by adding compost and worms.
March
Average day length: 9.5–13 hours (10.5–13 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 31–54°F (0–24°F in Alaska)
As the temperatures warm up, this is the point in your outdoor grow calendar to buy your seeds if you haven’t already! If you’re planning on cloning, your mother plant should be ready as the end of this month draws near.
For regular cultivation, you can start sprouting your seeds on the windowsill at the end of the month. Remember to keep an eye on the day length to ensure that your seedlings get enough sunlight.
Since most of the country won’t receive much daylight during this time anyway, we recommend using a lamp to provide additional light. Just a few hours each day will prevent your plants from entering the flowering stage prematurely.
A bonus tip from our marijuana outdoor grow guide calendar: If you’re cultivating autoflowers and want more than one yield, start sprouting your first batch of seeds now. If you’re opting for a single harvest, then hold germination off for another month.
April
Average day length: 12.5–14.5 hours (13.5–15.5 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 35–62°F (24–45°F in Alaska)
As the longer days draw near, we’re reaching the flowering time of our outdoor grow calendar—when daylight reaches at least 14 hours, pack that grow lamp away as you won’t need it anytime soon.
Closer to the end of the month, it’s time to move your plants outdoors. Put them in a container, allowing them to absorb natural light outside and be moved indoors at night.
If you live in colder areas, ensure that the last of the frost has cleared before moving your cannabis plants outdoors. Your young plants won’t survive the cold, so if need be, wait the extra month to keep your plant safe.
If you’re cloning, your mother plant is now ready for you to make clones.
May
Average day length: 14–15.5 hours (15.5–17.5 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 52–72°F (40–61°F in Alaska)
Spring is in the air! The best part of any outdoor grow calendar starts around now. While the temperatures are warming up, be sure to keep a close eye out for the last few traces of frost.
If you’re focusing on autoflower seeds, expect them to start sprouting in the second half of the month. Since some areas in the Midwest and Alaska experience three short months of warmer weather, you must act fast to harvest your crop at the end of August.
June
Average day length: 15–16 hours (8.5–10.5 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 22–51°F (-8–12°F in Alaska)
This is the most active time for the outdoor cannabis grow calendar in the Northern states as plants experience their most development. You’ll see that your autoflower plants start developing flowers if you look closely.
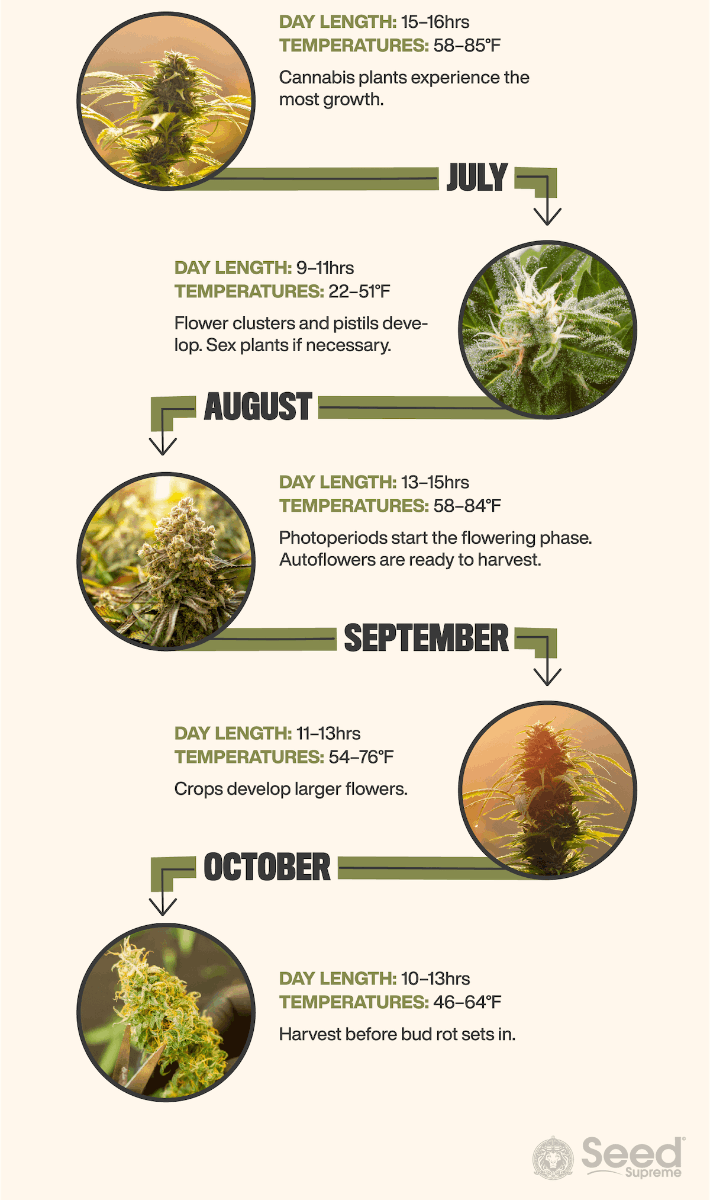
July
Average day length: 14–16 hours (16.5–18 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 58–85°F (55–73°F in Alaska)
As the hottest month in your outdoor grow calendar, your autoflower plants start developing large flower clusters. If you’re cultivating a photoperiod crop, you’ll see pistils forming.
If you’ve chosen to use regular seeds and don’t plan to breed, watch out for signs of male plants. You’ll identify male plants by the flowerheads developing on the side of the branch. Females present as drop-shaped leaves with two prominent white pistils.
August
Average day length: 13–15 hours (14–16.5 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 58–84°F (49–66°F in Alaska)
Your beloved autoflower crop is now drawing to the end of its outdoor marijuana grow calendar. Harvest your crops by cutting the flower heads and hanging them in a dark space to dry for ten days at room temperature. If the branch cracks when you bend it, you’re good to go.
Your photoperiod plants are now entering the flowering stage as most areas experience less than 14 hours of daylight.
September
Average day length: 11.5–13.5 hours (11.5–14 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 54–76°F (38–55°F in Alaska)
As the outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern US draws to a close, you’ll find that photoperiod plants develop larger flower clusters.
During the flowering phase, your plants are more susceptible to mold and mildew, which could destroy your crop. Take great care to keep your plants dry during this time. If you experience wet days, we recommend that you move your plants indoors or create a shelter to keep them dry.
Be sure to provide a windbreaker, shelter, or bamboo support if your marijuana plants are exposed to strong winds. This will prevent unwanted damage to your precious crops.
October
Average day length: 10–13 hours (11.5–14 hours in Alaska)
Average temperature: 46–64°F (20–33°F in Alaska)
Many cultivators should take extra care during the final month of the outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern states. Growing in cold or wet regions can mean a particularly high risk of bud rot during this time.
Pay close attention and be ready to harvest if you catch the slightest sign of bud rot. It’s far better to harvest early and have a diminished cannabis quality than lose an entire crop.
Marijuana grow calendar: Southern USA states
As we’ve shown in our outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern US states, taking the time to prepare for your harvest is the key to success.
If you’re living in the Southern states, keep an eye on the frost, as this signifies the start of your outdoor grow calendar. The average temperatures covered in this section refer to Houston, Miami, and Los Angeles.

February
Average day length: 10.5–11.5 hours (11.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 49–80°F (64–81°F in Hawaii)
As the lack of frost signifies the beginning of the outdoor cannabis grow calendar, you should start gathering up your supplies. Start shopping around for the best outdoor marijuana strains for your area. Since many areas experience an extended growing season, it’s safe to look at sativa strains.
Should you choose to start sprouting indoors, ensure that you maintain the required temperature between 68–77°F. By investing in some CFL grow lights, you’ll ensure the required temperature and light to sprout your seeds.
You should also take advantage of this time to ensure that you have the best soil for outdoor weed. Prepare your soil, adding compost and worms to loosen it up after the frost clears.
March
Average day length: 11.5–12.5 hours (11.5–12.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 50–81°F (68–82°F in Hawaii)
As the days start to feel significantly warmer, it’s time to kickstart your outdoor grow calendar if you haven’t already. Start sprouting your chosen seeds on your windowsill, ensuring that they receive at least 12 hours of sunlight.
This is where you must tread very carefully. If the daylight hours are less than 12 hours, you’ll need to make use of a grow lamp to prevent premature flowering.
Have you opted to work with clones? Take special care of the mother plant during this time if you plan on using your clones outdoors.
April
Average day length: 12.5–13.5 hours (12.5–13 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 55–84°F (70–83°F in Hawaii)
With rising temperatures, you’ll also find that April brings longer days in most areas. If you haven’t started yet, this is the ideal time in your marijuana grow calendar for outdoor sprouting.
If your daytime temperatures reach around 70°F, feel free to take your green babies outside. Just remember to bring them indoors in the evenings as it’ll be too cold and damage your seedlings.
This is the perfect time to start making clones from your mother plant.
May
Average day length: 13–14.5 hours (13–13.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 60–87°F (71–85°F in Hawaii)
At this point in your outdoor grow calendar, it’s warm enough to leave your cannabis plants in the garden safely.
If you’re opting for autoflower seeds, start planting them around the middle of the month. With enough sunlight and ideal temperatures, you’ll be ready to harvest your autoflower crop by the beginning of August.
June
Average day length: 14.5 hours (13.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 60–91°F (74–87°F in Hawaii)
This is the busiest time of your outdoor cannabis grow calendar, when your plants develop the most—especially from 18th–24th June. You’ll find that photoperiod plants grow faster, while autoflowers start to develop their flowers.
July
Average day length: 13.5–14.5 hours (13–13.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 65–93°F (75–88°F in Hawaii)
During the hottest month of your marijuana grow outdoor calendar, you’ll see flower clusters appear on autoflower plants and pistils on photoperiod ones.
If your goal is a quality yield instead of more seeds, keep an eye out for those pesky male plants. Look for pollen sacs to identify male plants and remove them as soon as possible.
August
Average day length: 13–14 hours (12.5–13 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 65–95°F (75–89°F in Hawaii)
If you planted autoflower seeds in May, then your outdoor cannabis grow calendar has come to an end. Cut the flower heads off and hang them in a dark room to dry to harvest your autoflower crop. Your marijuana will be ready in ten days if you maintain room temperature. The clear sign that your cannabis is ready is when the branch cracks if you bend it.
For photoperiod plants, you’re heading into the final part of the flowering phase of your outdoor grow calendar. If your plants receive less than 14 hours of light per day but need more time, bring them indoors under a lamp.
Remember to keep your photoperiod plants dry during this time to avoid bud rot, mold, and mildew. You should also take extra precautions to shield your plants from potentially damaging winds.
September
Average day length: 12–13 hours (12–12.5 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 64–89°F (75–89°F in Hawaii)
As September draws to a close, so does your outdoor marijuana grow calendar. As the days grow shorter and colder, you should prepare to harvest your crops.
As noted in the outdoor cannabis grow calendar for Northern states, you should watch for signs of bud rot. If there’s any indication of trouble, harvest your crop immediately to avoid losing everything. Rather a low yield than none.
October
Average day length: 11–12 hours (11.5–12 hours in Hawaii)
Average temperature: 60–86°F (74–87°F in Hawaii)
The start of Fall indicates the end of your outdoor grow calendar. If your plants aren’t entirely ready for harvesting yet, pay close attention to signs of damage—especially if you live in cold, wet areas—to avoid mildew, mold, or bud rot.
FAQs about marijuana grow calendars
Do you still have unanswered questions after reading our outdoor cannabis grow calendar? Here are a few of our frequently asked questions that’ll help shed some light.
How long does it take to grow a marijuana plant?
On average, marijuana seeds take 10–32 weeks (3–8 months) to complete a full life cycle.
If you want to speed up the process, we recommend that you start with a clone or use autoflower seeds. We should note, however, that these aren’t the best options if you’re new to cultivating.
When is the best time to grow marijuana?
If you’re outdoors, you should buy your seeds around February, starting them no later than the end of April. Depending on how cold and wet your area is, you should aim to harvest between the end of August and October.
For autoflower seeds, you should start your plants no later than the end of May and be ready to harvest by the end of August.
Which are the best strains for Northern and Southern states?
Since each strain has specific requirements, we cannot expect a seed that thrives in the North to do the same in the South. That said, our recommendations for the top strains to cultivate in the Northern states include:
The top strains for the Southern sates include:
Why are my outdoor plants flowering too early?
If your plants aren’t getting enough light during the day, they’ll flip into flower prematurely. If your daylight hours are shorter than required, move the plants indoors in the evenings and put them under a CFL grow lamp.
Timing is everything
With almost every state experiencing different weather conditions, it’s impossible to provide the exact scenarios for an outdoor grow calendar. We’ve based the information provided on an estimation for each region.
Pay close attention to the climatic conditions of your state before you start growing. Generally, marijuana thrives in moderate temperatures and plenty of sunlight. Head over to Seed Supreme to find the best high-yielding strains for your state.

 THC
THC