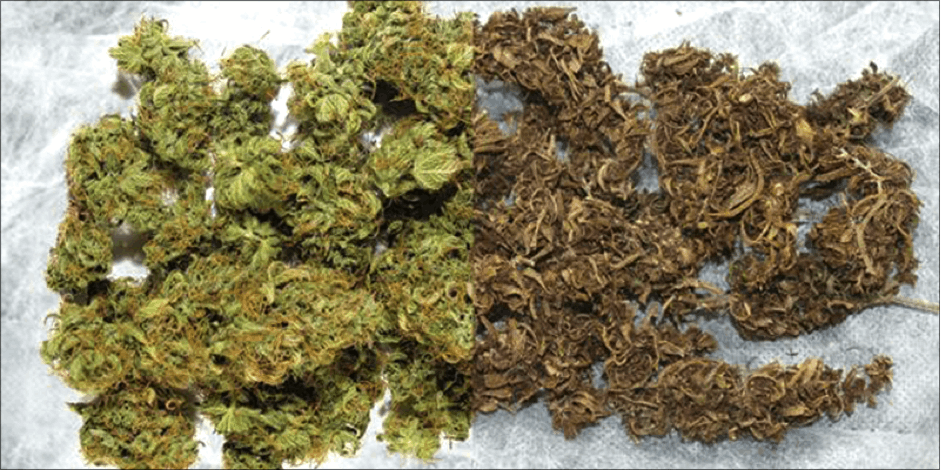
Growing indoors is hard - until it isn’t. Back in the old days, you would have to read books and do trial & error to get good at growing. These days, you just need one of the best cannabis seeds, a great…
Read more SeedSupreme Blog - Explore the wonderful world of Marijuana
- Posted on 2025-03-27 17:00:00
- Posted on 2023-09-03 17:00:00THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids in marijuana attach to the receptors in the brain’s ECS. These compounds may alter the way the system regulates endocrine functions and other factors affecting PMS. We…Read more
- Posted on 2023-08-30 17:00:00Marijuana can certainly help with chronic back and nerve pain. Weed strains contain numerous cannabinoids, the crucial elements responsible for its effects. These cannabis variants have properties that…Read more
- Posted on 2023-03-14 17:00:00What does your autoflower’s pot size have to do with your potential cannabis yield? Potting is a crucial decision that greatly impacts cannabis growth. Choosing the right container size for your autoflower…Read more
- Posted on 2023-02-14 16:00:00What’s the best way to germinate autoflower seeds? If it’s your first time sprouting them, you may be overwhelmed by the conflicting instructions available online. Fear not; we’re here to provide a comprehensive…Read more
- Posted on 2023-02-13 16:00:00Cannabis may sometimes cause giggle attacks, but what if it could make you laugh even before smoking it? We’ve got some of the funniest weed names that’ll crack you up so much you might need new pants…Read more
- Posted on 2023-02-13 16:00:00Are you wondering how to get bigger yields from autoflowers? These crops flower according to their age instead of depending on a light cycle. Due to their quick maturity rates, they require skilled hands…Read more
- Posted on 2023-02-06 16:00:00Is your grow op facing time or space constraints? You can LST autoflower plants to get photoperiod-tier yields while honoring the restrictions. Low-stress training is an easy and effective way to increase…Read more
- Posted on 2023-02-05 16:00:00Whether you make your own edibles from home grown weed or purchase the finest store-bought treats money can buy, you want them to last as long as possible. More often than not, a batch of cannabis edibles…Read more
- Posted on 2023-01-02 16:00:00Do you long for an abundant harvest of cannabis nugs but lack the necessary space? Perhaps you have an empty windowsill pot that’s just lying around. This guide shows you how to cultivate marijuana plants…Read more
- Posted on 2023-01-02 16:00:00Welcome to our weed measurements guide, where we explain which weighty words await you in your local cannabis dispensary. Users adopted slang that shaped cannabis culture, often for stealth reasons and…Read more
- Posted on 2022-12-19 16:00:00Has trying to choose from the plethora of cannabis seeds available made you confused? One of the most crucial factors in achieving a rewarding marijuana harvest is your decision between an autoflower vs.…Read more
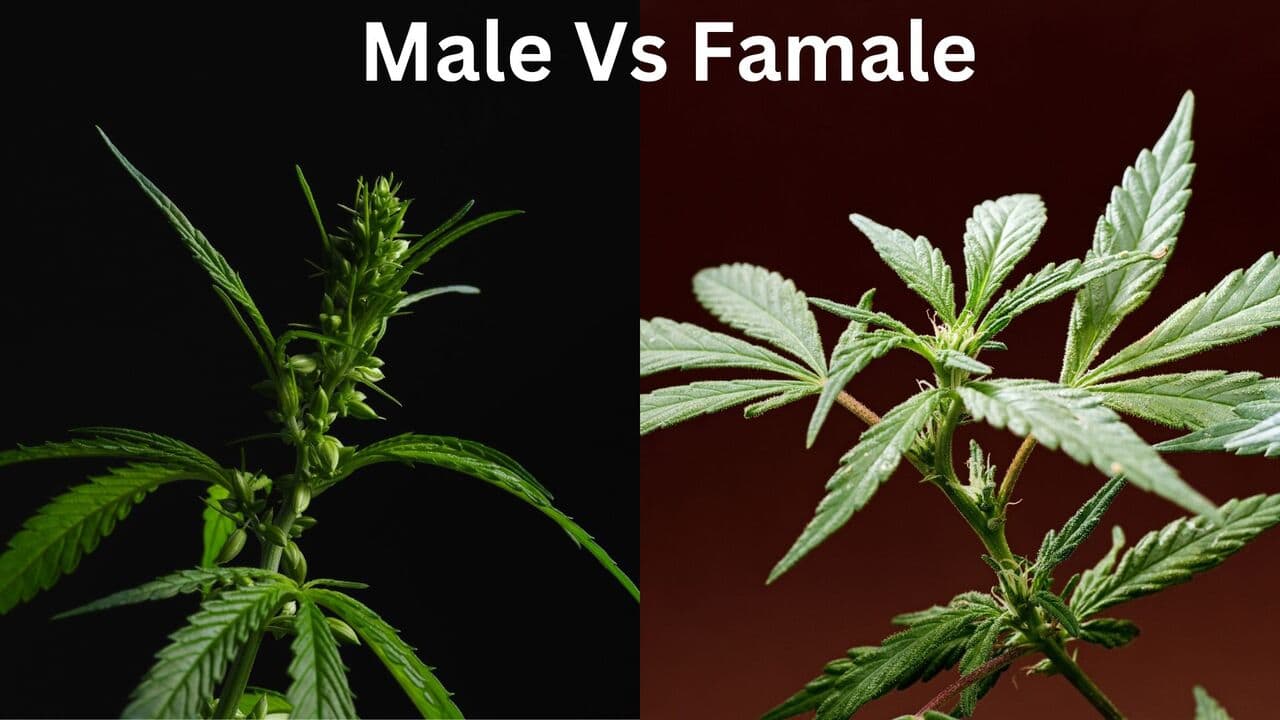
- Posted on 2022-12-19 16:00:00Are you interested in growing cannabis or harvesting and finding unwanted seeds in your buds? Understanding male vs. female weed plants is essential in cultivating marijuana. Learning to spot the differences…Read more
- Posted on 2022-12-18 16:00:00Your cannabis crops have just finished vegging and suddenly experience a vertical growth spurt. Why? Is it normal? When do your plants stop stretching in flower? This sudden growth is entirely normal…Read more
- Posted on 2022-12-18 16:00:00Did you know that the cannabis flowering stage is when plants produce resinous buds? They undergo hormonal changes that trigger the development of wispy pistils (white hairs) and bud sites in this phase.…Read more
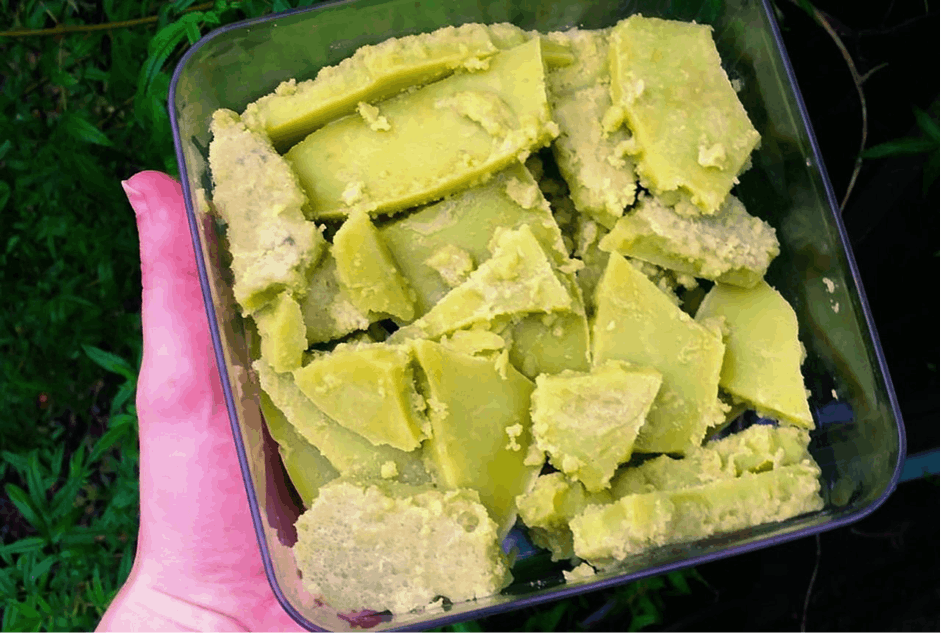
- Posted on 2022-12-15 16:00:00Have you been enjoying hash in your joint or by dabbing? Inhaling weed in this form is a popular method of consumption, but did you know you can infuse it in your food? Learning how to make hash butter…Read more
- Posted on 2022-12-15 16:00:00Have you got a couple of buds that seem too dry to smoke? It’s a common problem for the last few nugs in a big batch. Fortunately, learning how to rehydrate weed is relatively simple. There are several…Read more
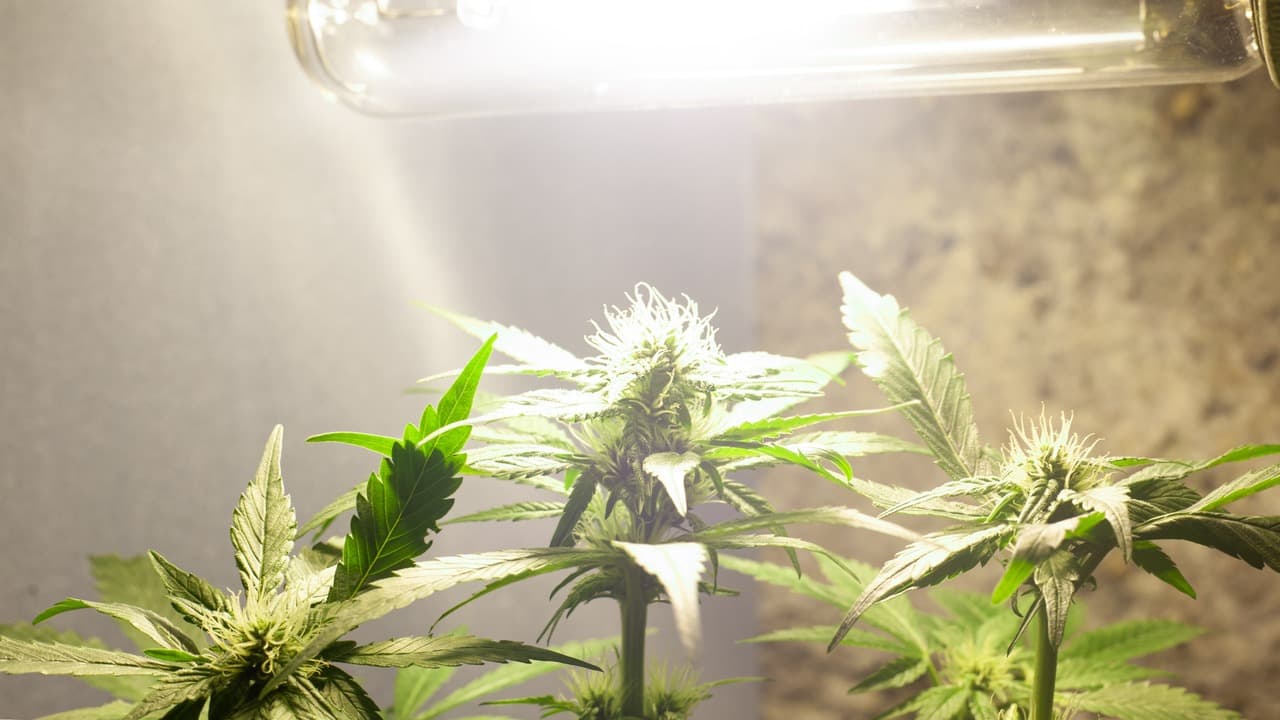
- Posted on 2022-12-08 16:00:00How much light does a weed seed need? What’s the ideal quantity of rays to provide marijuana plants at different stages of growth? These are common questions among cannabis cultivators. Weed has special…Read more
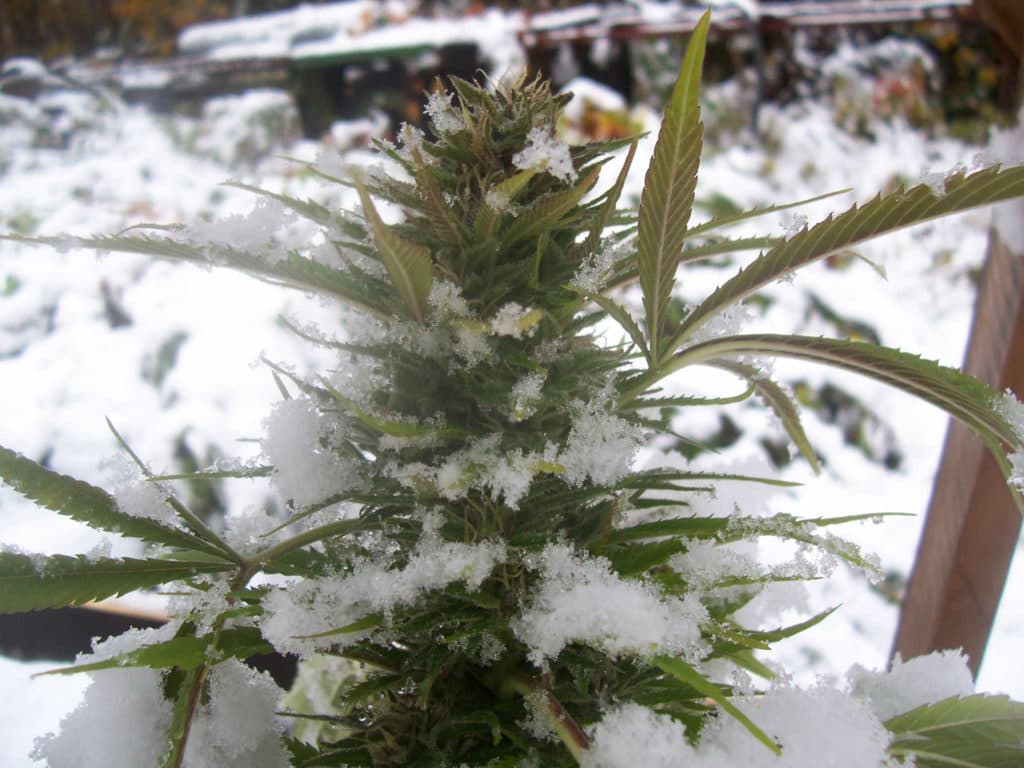
- Posted on 2022-12-08 16:00:00Have you considered cultivating indoor or outdoor winter strains? Planting cannabis during colder weather can be straightforward and rewarding, provided you create the ideal environment and use marijuana…Read more

 THC
THC